Maternal mortality in the United States has emerged as a pressing public health crisis, leading the nation to record alarmingly high maternal mortality rates compared to other high-income countries. Between 2018 and 2022, the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths continued to escalate, underscoring a dire need for enhanced prenatal care and postpartum support. These alarming trends are exacerbated by significant racial disparities in maternal health, where women of color face disproportionately higher risks. Cardiovascular disease during pregnancy has been identified as a primary factor behind these fatalities, accounting for a substantial proportion of deaths. Addressing maternal mortality in the United States requires urgent systemic changes and targeted interventions aimed at minimizing preventable complications and ensuring equitable healthcare access for all women.
The issue of pregnancy-related deaths in America reflects broader challenges within maternal health care, emphasizing a need for reform to tackle risks during and after childbirth. The rising fatalities among new mothers highlight serious gaps in medical support, both prenatally and during the postpartum phase, which must be bridged to reverse this alarming trend. Particular attention is necessary for specific demographics experiencing elevated risks, as evidenced by the disparities faced by racial and ethnic minorities. Moreover, the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular problems among pregnant women necessitates an urgent response from healthcare providers to improve management strategies and extend necessary care. Ultimately, ensuring safe pregnancies and reducing mortality rates requires comprehensive policy changes and a recommitment to maternal health initiatives.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the United States
Maternal mortality in the United States has reached alarming levels, especially when compared to other high-income countries. With the highest maternal mortality rate among its peers, the U.S. sees a disturbing continuation of rising pregnancy-related deaths. Such a trend highlights the urgent need for healthcare reform, particularly concerning factors like prenatal and postpartum care. More than 80 percent of these fatalities are reportedly preventable, underscoring that systemic changes are critical to improving maternal health outcomes.
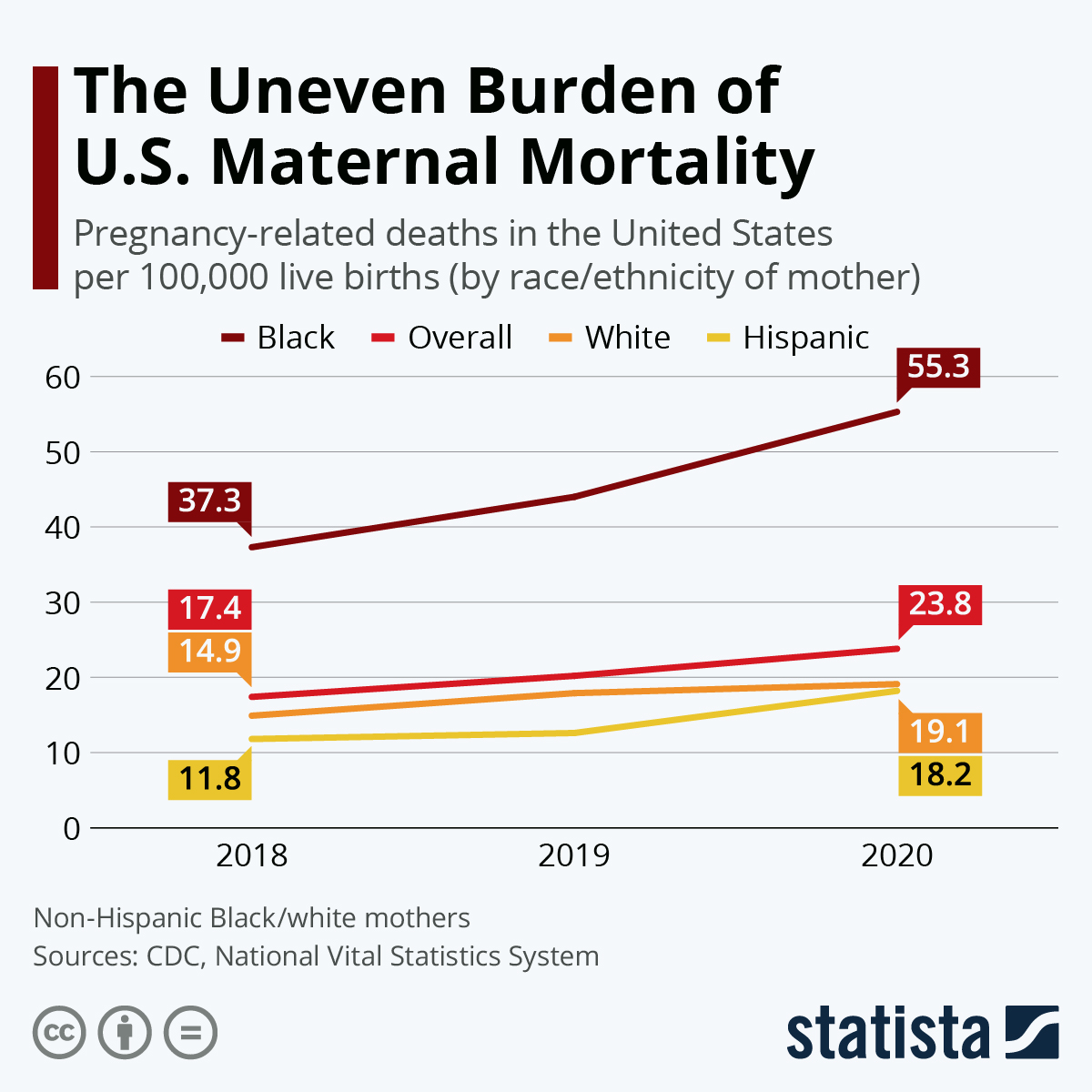
The stark inequalities in maternal mortality rates are particularly concerning. Data reveals that American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than those of white women. This statistic shines a light on the racial disparities in maternal health, demonstrating a persistent gap that calls for immediate action. To combat this issue, addressing biases within the healthcare system and creating equitable policies will be essential in the journey toward significant improvements in maternal mortality.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Maternal Mortality
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of maternal deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20 percent of pregnancy-related fatalities. Historically, complications like hemorrhage were the primary concerns; however, the shift towards cardiovascular issues indicates a need for enhanced screening and management of chronic conditions in expectant mothers. As younger individuals—especially those aged 25 to 39—are now experiencing these health problems, it raises alarm bells regarding early detection and preventive care.
Given the complexity of cardiovascular disease, comprehensive knowledge about its effect on pregnancy is vital. Conditions such as hypertension and pre-eclampsia require careful monitoring and management throughout the prenatal and postpartum periods. The increasing prevalence of these issues among younger populations points to the necessity of establishing better healthcare practices tailored to address the specific needs of expectant mothers. By doing so, the risk of maternal mortality linked to cardiovascular disease can be reduced significantly.
Addressing Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial disparities in maternal health continue to be a pressing issue in the United States, with significant differences highlighted in recent studies. The mortality rates among non-Hispanic Black women are alarmingly high compared to their white counterparts. This disparity is compounded by systemic risks inherent in the healthcare system, such as bias, inadequate access to quality prenatal care, and socioeconomic challenges that disproportionately affect communities of color. Broadening access to comprehensive healthcare services could be a key step in mitigating these disparities.
Efforts to reduce racial inequities in maternal health outcomes are imperative. This includes implementing culturally competent care practices, investing in community health resources, and ensuring that all women, regardless of race or socioeconomic status, receive adequate access to prenatal and postpartum care. By tackling these systemic issues, we can work towards a more equitable healthcare landscape that promises better outcomes for all mothers.
The Importance of Postpartum Care Improvements
Postpartum care is critical in addressing maternal health, yet it often receives insufficient attention within the healthcare system. Many policies and protocols frame the postpartum period as a distinct six-week phase, neglecting the extended recovery time many women experience. The recent findings indicate that nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after delivery. This emphasizes the need for a shift in focus towards improved care that extends beyond the immediate postpartum phase.
Improving postpartum care requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses mental health, physical health monitoring, and accessibility to resources during the recovery period. Implementing continuous care models will not only save lives but will also enhance overall maternal health. Building awareness and creating guidelines that acknowledge the significance of the entire postpartum year can lead to substantial improvements in preventing pregnancy-related deaths.
Public Health Infrastructure and Maternal Care
The state of public health infrastructure in the U.S. is an essential aspect to consider regarding maternal mortality rates. Research suggests that inadequate funding and prioritization of maternal health initiatives are directly related to rising pregnancy-related deaths. Increased investment in effective public health measures is crucial for tracking, analyzing, and improving maternal health outcomes nationwide. Without robust infrastructure, efforts to understand the problem and propose viable solutions are severely hampered.
Advocacy for enhanced public health funding is paramount, especially in light of recent budget cuts affecting maternal health programs. Ensuring ongoing support for maternal health research and public health initiatives is essential for developing evidence-based policies that address the underlying issues of high maternal mortality rates. By solidifying the public health foundation, we can implement effective strategies to enhance both maternal and infant health across the United States.
Innovative Solutions to Combat Maternal Mortality
Innovative solutions are necessary to confront the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. Integrating technology and data-driven approaches to identify at-risk populations could vastly improve prenatal and postpartum care. Telehealth services, for instance, can offer immediate access to medical professionals, making support more inclusive and widespread. Such initiatives empower women, particularly those in underserved regions, by providing them with timely guidance and resources necessary to navigate their pregnancy journey safely.
Additionally, promoting community-based health programs that focus on education and early intervention can create a significant positive impact on maternal health outcomes. By fostering collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations, tailored solutions that address specific local needs can be developed. Harnessing the strength of community resources can ultimately lead to a more holistic approach in tackling the challenges of maternal mortality.
State-Level Variations in Maternal Mortality
State-level variations in maternal mortality rates illustrate the disparities that exist within the U.S. healthcare system. Research indicates that improvements in states like California exemplify what is possible through focused health initiatives and comprehensive maternal care frameworks. By studying and replicating successful strategies from states with lower mortality rates, other regions can enhance their maternal health outcomes significantly. Understanding the reasons behind these variations is a critical step in developing effective policies that address the unique needs of each state.
Furthermore, the role of state policies in shaping maternal health cannot be underestimated. Each state’s approach to healthcare access, insurance coverage, and support for maternal care directly affects outcomes. Stakeholders must advocate for policies that prioritize maternal health, including expanded insurance coverage for prenatal and postpartum care. By fostering a culture of constant improvement and commitment to quality maternal healthcare, states can work towards reducing the significant disparities that currently exist.
The Impact of Chronic Conditions on Maternal Health
Chronic conditions pose a significant risk to maternal health and are increasingly present in younger populations. With issues like hypertension and cardiovascular disease becoming more common among pregnant women, it is imperative to prioritize the management of these conditions through ongoing healthcare strategies. This entails improving wellness initiatives that focus on monitoring and reducing health risks well before pregnancy. By capturing data on pre-existing conditions, healthcare providers can enhance their pregnancy care protocols.
Furthermore, education surrounding chronic health issues in pregnant women can help mitigate potential risks. Equipping expectant mothers with strategies to manage their health conditions can vastly improve outcomes. This integrated approach to maternal care will not only address pregnancy-related deaths effectively but can also contribute to overall well-being, fostering healthier generations to come.
The Need for Comprehensive Maternal Death Tracking
An effective system for tracking maternal deaths is crucial for understanding and improving maternal health in the United States. The integration of a pregnancy checkbox on death certificates was a significant step toward gathering accurate data about maternal mortality. However, challenges remain in maintaining complete and timely reporting of these death rates across all states. Ensuring that states adhere to uniform tracking practices will generate reliable data essential for informed decision-making regarding maternal health initiatives.
Advocating for thorough data collection and research funding is necessary to highlight the pressing issues surrounding maternal mortality. A comprehensive understanding of the demographics, causes, and circumstances of maternal deaths offers insight into necessary policy reforms. By investing in effective tracking systems and ongoing research, stakeholders can work collaboratively to develop strategies that can significantly reduce maternal fatalities in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary reasons for high maternal mortality rates in the United States?
The United States has a high maternal mortality rate compared to other high-income countries due to reasons such as a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable policies, and access issues like maternity care deserts. Additionally, systemic bias and discrimination against racial and ethnic groups contribute significantly to these pregnancy-related deaths.
How do racial disparities impact maternal mortality rates in the United States?
Racial disparities are a significant factor in maternal mortality rates in the U.S. American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate nearly four times higher than that of white women, with non-Hispanic Black women also experiencing disproportionately high rates. These disparities highlight persistent inequities within the healthcare system.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of maternal mortality in the United States, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. This trend reflects an increase in chronic conditions like hypertension among younger individuals, necessitating improved postpartum care and monitoring.
Why is postpartum care improvement important for reducing maternal mortality?
Improving postpartum care is crucial as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy, a period often overlooked by health systems. Enhanced care beyond the initial 6 to 12 weeks can significantly reduce maternal mortality risks and ensure better long-term health outcomes.
How has COVID-19 impacted maternal mortality rates in the United States?
The COVID-19 pandemic contributed to a sharp increase in maternal mortality rates during 2021, and while the rates dropped afterward, they remained higher than pre-pandemic levels. This highlights the need for focused maternal health policies during public health crises.
What steps can be taken to address the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Addressing the rising maternal mortality rates involves investing in public health infrastructure, enhancing quality of care during pregnancy and the postpartum period, and implementing policies that reduce disparities across states. It’s essential to prioritize maternal health and allocate research funds effectively.
What has changed in the tracking of maternal deaths in the United States since 2018?
Since the full implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates in 2018, tracking maternal deaths has improved significantly. This change has allowed for more accurate data collection on pregnancy-related deaths, helping identify trends and disparities in maternal health.
What is the significance of undocumented late maternal deaths in the U.S.?
Undocumented late maternal deaths, occurring up to a year postpartum, are significant because they highlight the need for continuous healthcare beyond the immediate postpartum period. Recognizing these deaths as maternal mortality emphasizes the ongoing healthcare challenges mothers face after childbirth.
What innovative solutions are suggested for improving maternal health outcomes?
Innovative solutions to improve maternal health outcomes include investing in quality care systems during pregnancy and extending support into the postpartum period. This includes training healthcare providers to recognize and treat emerging chronic conditions like hypertension, particularly in younger populations.
How can state-level policies influence maternal mortality rates?
State-level policies can greatly influence maternal mortality rates by establishing effective healthcare programs, addressing disparities, and ensuring equitable access to quality prenatal and postpartum services. Understanding why certain states perform better also helps implement best practices nationwide.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, continuing to rise from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable with proper care. |
| Disparities by Race and State | American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate of 106.3 per 100,000 live births, significantly higher than white (27.6) and non-Hispanic Black women (76.9). |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in maternal mortality was in 2021, coinciding with the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Cardiovascular diseases are now the leading cause of maternal deaths, accounting for over 20% of fatalities. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly a third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, highlighting the need for extended care. |
| Need for System Improvement | Investment in public health infrastructure is crucial for addressing rising maternal mortality and improving care during pregnancy and postpartum. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the United States has become a critical public health issue, with the country facing alarming rates that surpass its high-income counterparts. As recent studies show, over 80% of these deaths are preventable, yet disparities persist across racial and state lines. To combat this troubling trend, a focused investment in quality prenatal care and extended postpartum support is essential, along with a commitment to addressing systemic inequities within the healthcare system. Only through targeted interventions can we hope to reverse the increasing maternal mortality trends in the United States.