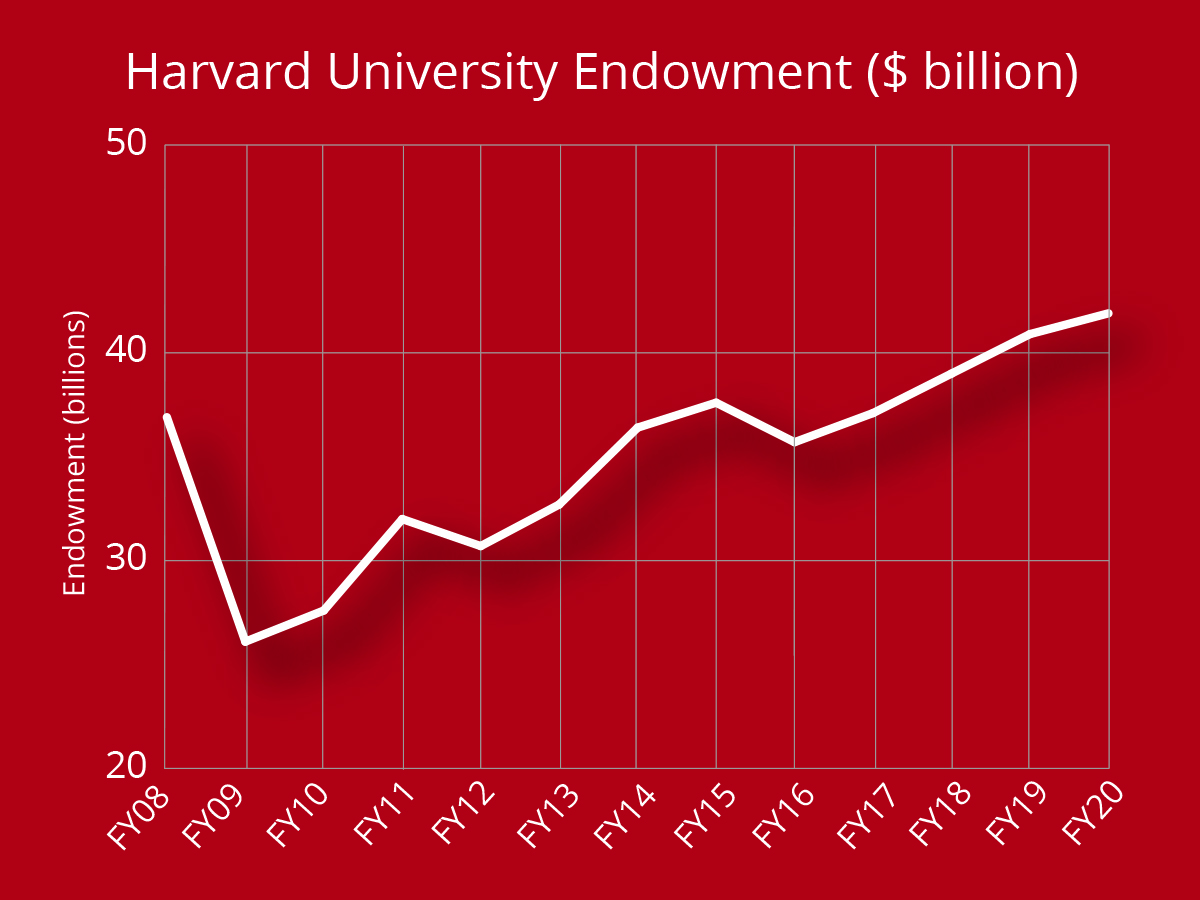
The Harvard endowment, with its impressive valuation surpassing $53 billion, serves as a crucial financial cornerstone for Harvard University. This hefty sum, while providing flexibility for various investments and operational needs, inherently comes with significant risks that require careful navigation. The complexities of endowment management mean that much of this wealth is tethered by donor restrictions, making the allocation of funds a delicate balancing act. Additionally, the ongoing dialogue regarding a potential Harvard budget deficit exacerbates concerns, as pressures mount to utilize the endowment for immediate financial aid at Harvard. Understanding these dynamics is essential for assessing the overarching endowment investment strategy and its implications for the university’s long-term financial health.
As discussions unfold around the financial sustainability of Harvard University, the topic of endowment risks takes center stage. The challenges of managing a financial reserve of this magnitude not only affect the institution’s operational budget but also impact strategic planning for future investments. Harvard’s financial landscape is punctuated by the need to address funding across various schools while ensuring adequate support for student financial aid programs. Moreover, the potential for economic downturns and cuts in federal funding raises important questions about how effectively the university can leverage its endowment to meet evolving needs. In navigating these complexities, Harvard must adopt a nuanced perspective on fiscal responsibility that considers both immediate and long-term financial outcomes.
Understanding the Harvard University Endowment Structure
Harvard University’s endowment is a complex financial structure that is crucial for funding a variety of academic and operational activities. With an endowment valuation of approximately $53 billion, the University boasts one of the largest endowment funds in the world. However, much of this endowment is stringently restricted by donor agreements, which means that not all of the funds can be utilized freely within the institution. The majority of the endowment is allocated to specific schools within Harvard, limiting the autonomy of University leadership to access these funds for urgent financial needs or to cover operational costs.
This intricate system creates a challenge for endowment management, where the restricted funds are primarily dedicated to predefined purposes such as scholarships, professorships, and research initiatives. While these allocations support the intellectual environment of the institution, they also complicate Harvard’s ability to navigate fiscal deficits and immediate funding crises. The flexibility that the endowment offers is significantly constrained, as only a small fraction—less than 5%—remains unrestricted for general use. Understanding this structure is vital for grasping the underlying risks associated with the endowment and how it impacts Harvard’s long-term financial strategy.
Balancing Immediate Needs with Long-Term Planning
The conversation around Harvard’s endowment often highlights the tension between responding to immediate financial needs and maintaining a stable long-term investment strategy. University leaders face decisions that can significantly affect the institution’s financial health. For instance, tapping into the endowment to cover deficits poses risks that can lead to greater hardships in the future. An economist’s perspective on this matter emphasizes the importance of thoughtful financial strategizing, particularly when time is a luxury that endowment management provides.
When Harvard encounters financial uncertainty, whether from rising operational costs or external funding pressures, the decision to allocate resources from the endowment demands careful consideration. Although drawing more on the endowment may alleviate short-term challenges, it results in diminished financial flexibility down the road. Harvard’s historical reliance on a well-planned payout strategy—aiming for consistent returns while accounting for inflation—has served to stabilize its financial ecosystem. Yet, with variabilities such as economic downturns or crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, there is a pressing need for a robust framework that enables Harvard to navigate both immediate and future challenges effectively.
Risks Associated with the Harvard Endowment Management
While the Harvard University endowment provides essential resources for the institution, it carries inherent risks that can impact its ongoing sustainability. The potential for external factors—like policy changes from the government or variations in financial markets—poses significant risks to the stability of the endowment’s value and its ability to generate income. For example, the threat of losing federal tax-exempt status or facing cuts in research funding jeopardizes the revenue stream that Harvard relies upon. This creates an anxious scenario where strategic investment decisions might clash with the pressing need for immediate funding.
As noted by experts in endowment management, it is crucial for Harvard to adopt a rigorous approach to scenario analysis in order to prepare for potential adverse outcomes. By evaluating what the future might hold—whether it’s a tax imposed on endowment gains or a permanent drop in sponsorship funding—University leaders can strategize appropriate long-term adjustments. Such proactive measures are vital for mitigating risks and ensuring that the endowment continues to support Harvard’s mission while navigating unpredictable financial waters.
Impact of External Economic Factors on Harvard’s Endowment
The financial landscape in which Harvard operates is not static; it is greatly influenced by a multitude of external economic factors. Events like financial crises, inflation surges, or significant policy shifts can directly affect the performance of the Harvard endowment and, consequently, the resources available for financial aid and other key initiatives. For example, Harvard’s endowment, which strives for an 8 percent return, may falter if economic conditions cause market downturns, directly impacting the funds available for scholarships and operational costs.
Moreover, potential disruptions in federal funding—especially in the context of research grants—can create immediate budget deficits for the institution. When external funding sources dwindle, Harvard often turns to its endowment for support, revealing the delicate dance between maintaining a healthy endowment and meeting the urgent demands of the moment. This challenge emphasizes the need for strategic foresight in endowment management, to ensure that long-term investments are safeguarded against cyclical economic pressures.
Strategies for Effective Endowment Investment Management
Effective management of the Harvard University endowment requires a comprehensive investment strategy that balances risk and reward. Decision-makers must consistently refine their approach to asset allocation, ensuring a diversified portfolio that can withstand the pressures of market volatility. The overarching goal is to secure stable, long-term growth while also catering to the immediate financial needs of the University. Harvard’s management techniques involve a multi-faceted approach that includes assessing various asset classes and their potential returns, considering historical performance, and continuously adapting to changing economic climates.
Integral to this strategy is an understanding of how endowment investments translate into tangible benefits for Harvard community members, particularly through financial aid programs. By generating consistent returns, the endowment supports an academic environment that prioritizes accessibility and affordability. However, the balancing act involves cautious spending: University leaders must ensure that the distribution from the endowment does not undermine future growth prospects. The ongoing challenge lies in crafting a financial narrative that optimizes the endowment’s benefits for current and future generations.
The Role of Harvard’s Endowment in Financial Aid Policies
One of the most critical functions of Harvard’s endowment is its role in funding financial aid programs that provide support to students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. The University prioritizes accessibility and affordability, ensuring a high-quality education is within reach for talented students regardless of their financial situation. With a significant portion of the endowment allocated to this purpose, it helps subsidize tuition and provide generous grants, making Harvard one of the leading institutions for financial aid.
However, financial aid impacts the endowment’s overall revenue generation, as the funds used for this purpose reduce the amount available for operational costs and other investments. While it is commendable that Harvard can offer such support, endowment management requires constant vigilance in order to maintain a balanced budget. As the economic landscape shifts, University leaders must evaluate their financial aid policies and how they align with the sustainability of the endowment, ensuring that it can continue to serve its critical function in the long run.
Navigating Budget Deficits Through Strategic Endowment Use
In times of budget deficits, Harvard University often relies on its endowment as a financial lifeline. The ability to withdraw funds from the endowment can be a strategy employed to alleviate immediate fiscal pressures, but this must be done cautiously. Drawing from the endowment can provide essential resources for covering operational expenses or unexpected costs caused by external shocks, but such measures can also impact long-term financial health.
University leaders must engage in strategic decision-making when it comes to utilizing the endowment during budget deficits. This involves carefully assessing the potential long-term implications of depleting endowment resources—while addressing current needs, they must ensure that future financial stability is not jeopardized. It’s crucial to implement a balanced approach that addresses both immediate financial concerns and long-term sustainability.
Confronting Challenges to Harvard’s Endowment Stability
The stability of Harvard’s endowment is increasingly challenged by a combination of external pressures and internal dynamics. As the political landscape fluctuates, issues such as potential taxation of endowment funds and decreases in government funding for higher education present formidable obstacles. These challenges necessitate a reevaluation of how the endowment is managed and strategized in order to protect the financial future of the institution.
Moreover, the unpredictable nature of global markets introduces further volatility into the endowment’s performance. Events such as economic recessions or dramatic shifts in investment landscapes can force university leaders to rethink their financial strategies. A robust framework for risk management must be developed, one that not only anticipates these challenges but also provides pathways for sustainable growth and operational viability.
Evaluating Future Trends in Endowment Management
The continual evolution of endowment management practices will be critical for Harvard to maintain its competitive edge in the higher education landscape. As universities face new challenges and opportunities arise, it is essential to regularly evaluate and adapt investment strategies. Trends such as sustainable investing are becoming increasingly relevant, as stakeholders demand responsible management of institutional funds that aligns with broader societal values.
Furthermore, the integration of technology and data analysis into endowment management presents a promising avenue for enhancing decision-making processes. Data-driven approaches can enable Harvard to model various financial scenarios and outcomes, thereby informing its investment strategies more effectively. By staying ahead of emerging trends, Harvard can ensure that its endowment remains a powerful tool for fulfilling its mission well into the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main risks associated with the Harvard University endowment?
The main risks associated with the Harvard University endowment include dependency on volatile investment returns, potential changes in federal funding, restrictions on spending due to donor stipulations, and the implications of a potential endowment tax. The endowment’s performance can be significantly affected by economic downturns, and any reduction in federal research grants could further complicate the financial landscape.
How does financial aid at Harvard relate to endowment management risks?
Financial aid at Harvard is closely tied to endowment management risks because a portion of the endowment’s annual distribution helps fund financial aid programs. As the university allocates increasing amounts for financial aid, it inadvertently depletes resources that could be used for other operations, posing a risk to long-term financial sustainability and operational flexibility.
In what ways can Harvard mitigate endowment management risks?
Harvard can mitigate endowment management risks by diversifying its investment strategy, carefully managing spending rates, and maintaining a robust financial planning process. Scenario analysis can help the university prepare for potential economic shifts and funding changes. Additionally, proactively managing donor expectations regarding fund restrictions can also protect the endowment’s flexibility.
What impact does a budget deficit have on the Harvard University endowment?
A budget deficit at Harvard can increase reliance on the endowment to cover operational costs, which poses a risk to long-term financial health. When the endowment is drawn upon to address budget shortfalls, it limits future spending capacity and can exacerbate financial challenges, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
What lessons can be learned from past endowment investment strategies at Harvard?
Past endowment investment strategies at Harvard highlight the importance of balancing short-term financial needs with long-term growth. An overdependence on current funds can lead to future budget constraints. Harvard’s focus on smoothing investment returns and using strategic financial planning can help mitigate the risks associated with endowment management.
How do external factors, like federal funding or tax status, pose risks to the Harvard endowment?
External factors such as changes in federal funding or the university’s tax-exempt status can significantly impact the Harvard endowment. A freeze or reduction in federal grants can create financial strain, while changes to tax policies could limit Harvard’s financial flexibility and overall funding capability, introducing new layers of risk.
What role does scenario analysis play in managing Harvard’s endowment risks?
Scenario analysis plays a crucial role in managing Harvard’s endowment risks by allowing university leaders to assess potential financial impacts of various adverse events, such as reduced federal funding or investments losses. This strategic approach enables informed decision-making concerning budget adjustments and long-term planning, essential for sustaining the endowment’s health.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Endowment Value | $53 billion, a record as of the fiscal year 2025. |
| Restricted Funds | Majority of endowment funds are donor-restricted and allocated to specific schools. |
| Unrestricted Funds | Less than 5% accessible for discretionary spending by university leadership. |
| Governance | John Y. Campbell, economist, emphasizes careful long-term planning amidst immediate pressures. |
| Financial Risks | External shocks can strain finances, leading to increased endowment distributions for operational expenses. |
| Scenario Analysis | University leaders must evaluate potential impacts of lost funding and tax status. |
| Long-term Planning | Necessary adjustments in spending or revenue generation due to changing future conditions. |
Summary
Harvard endowment risks are a pressing concern as the university navigates its financial landscape. The substantial endowment of $53 billion, while a significant asset, conceals complexities such as extensive limitations imposed by donor restrictions and the reality that only a small fraction is available for discretionary use. As external challenges arise, including potential federal funding freezes and shifts in tax-exempt status, the university’s dependence on its endowment for operational stability becomes increasingly precarious. To ensure sustainability, Harvard must adopt a strategic approach to balance immediate financial needs with careful long-term management, acknowledging that present decisions may impact future resources.